Gabriela Bulisova & Mark Isaac
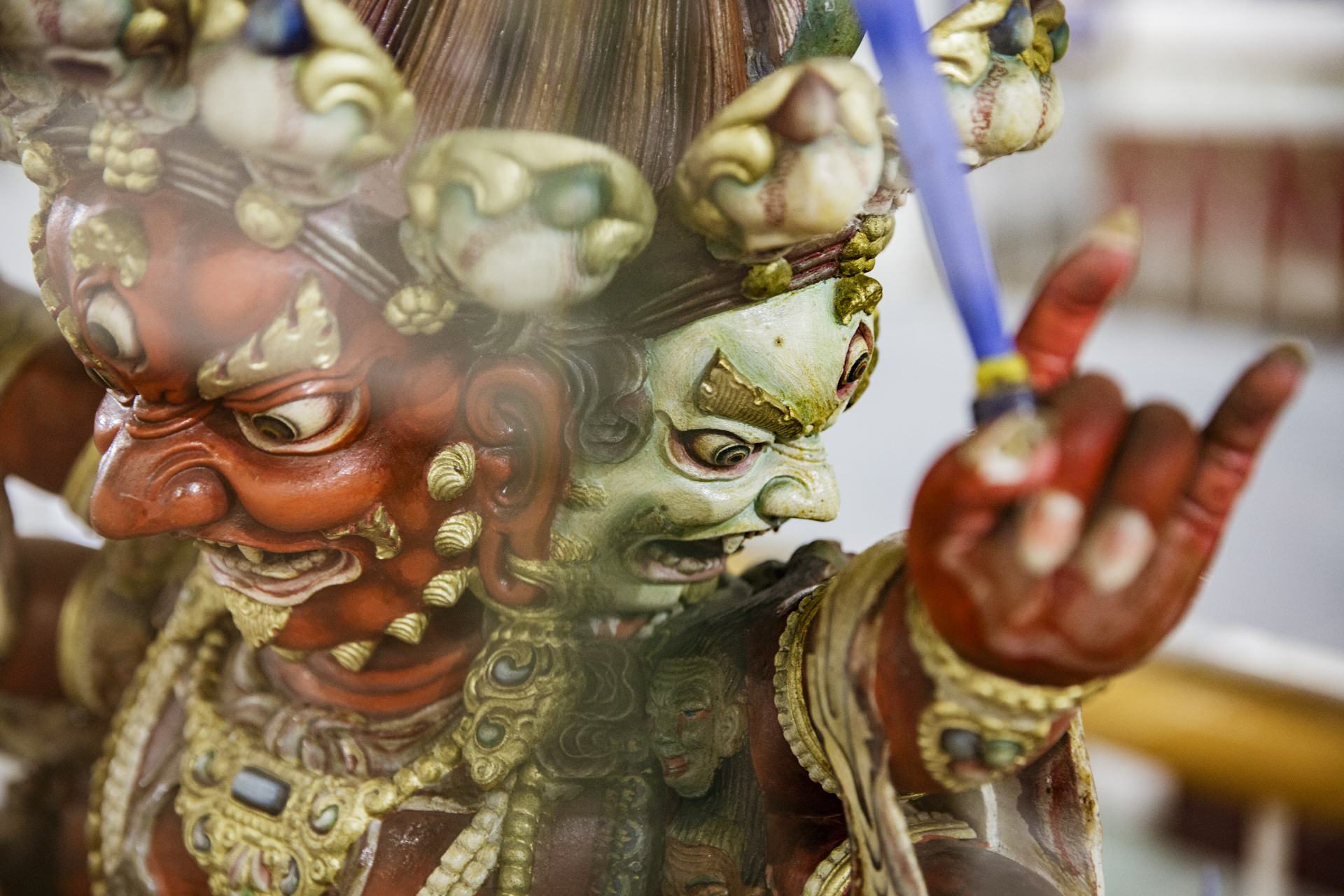
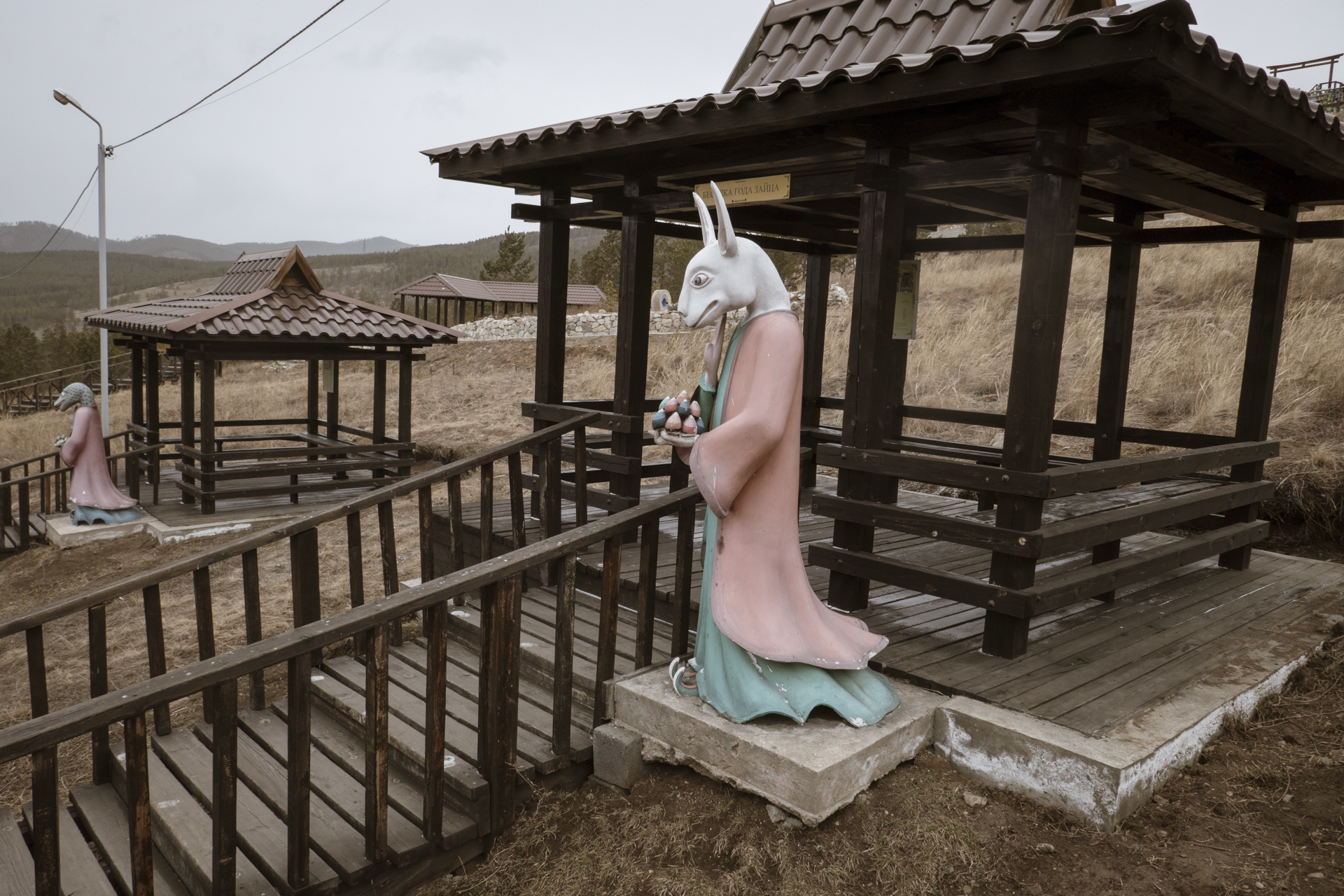






















At a time of polarization and division around the world, the Republic of Buryatia stands out as a place where people of diverse backgrounds live in harmony. Ulan-Ude, the tranquil and welcoming capital nestled among a ring of mountains, is not only the leading center of Buddhism in Russia, but a haven for those practicing Shamanism, the Russian Orthodox faith, and for Old Believers, who maintain the ancient rituals of the Orthodox church before reforms were implemented centuries ago. And each of these faiths places a high value on the land, air, and water.
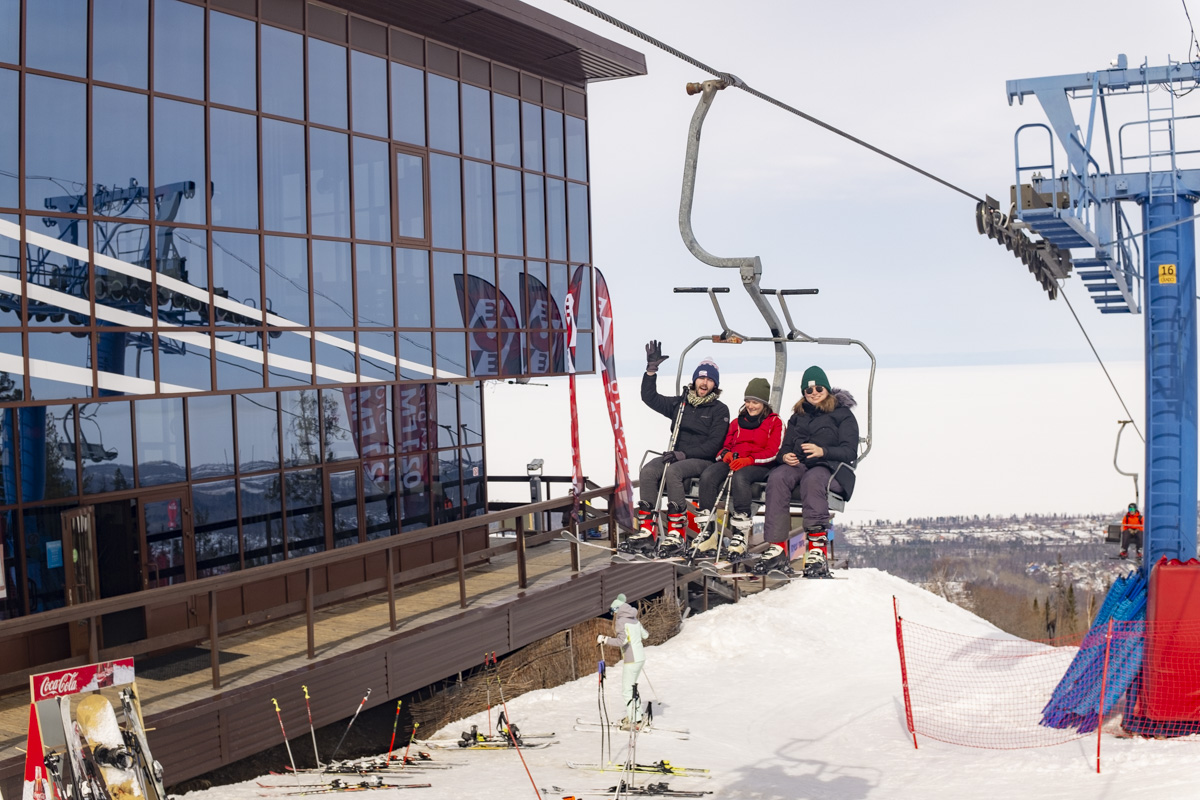
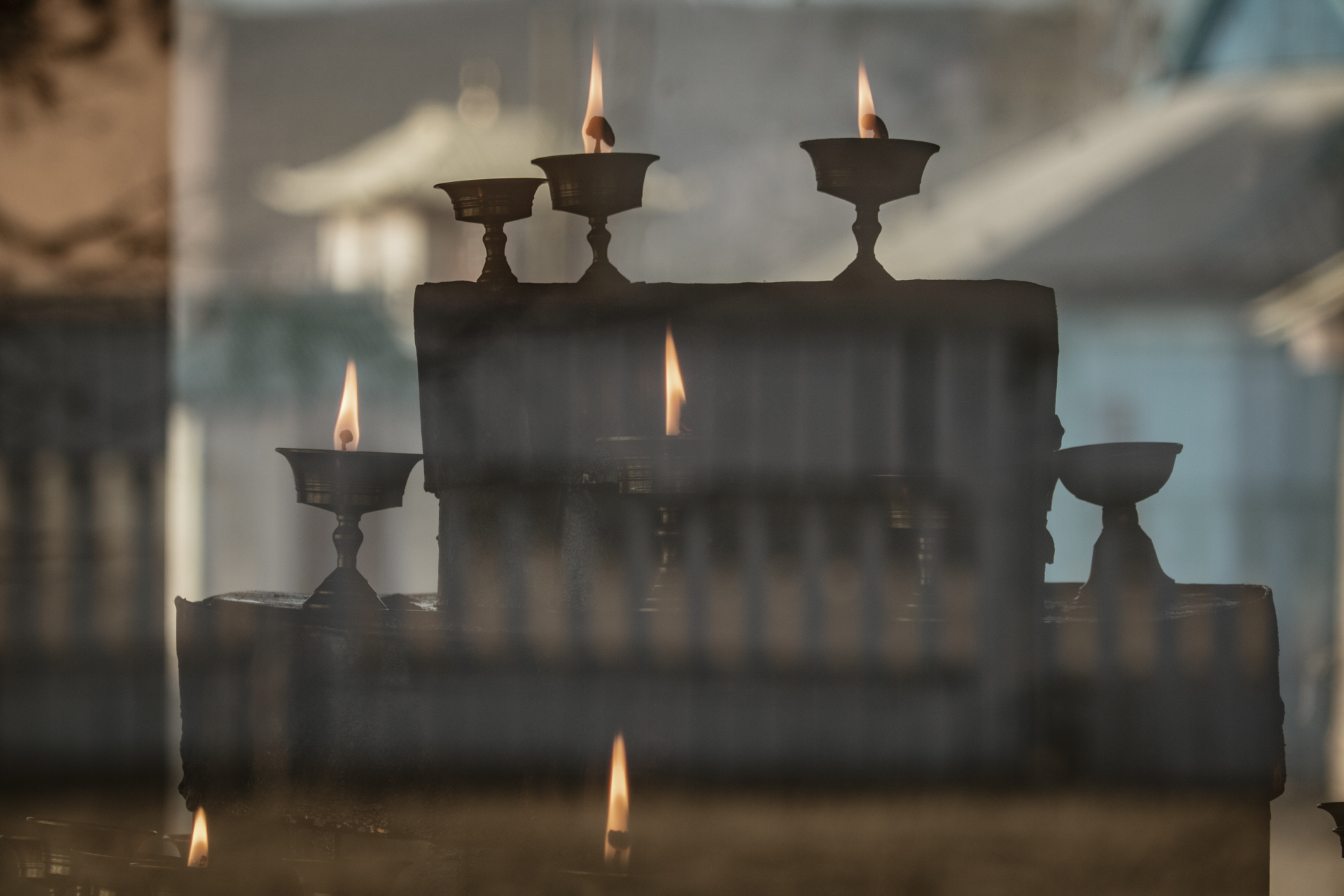
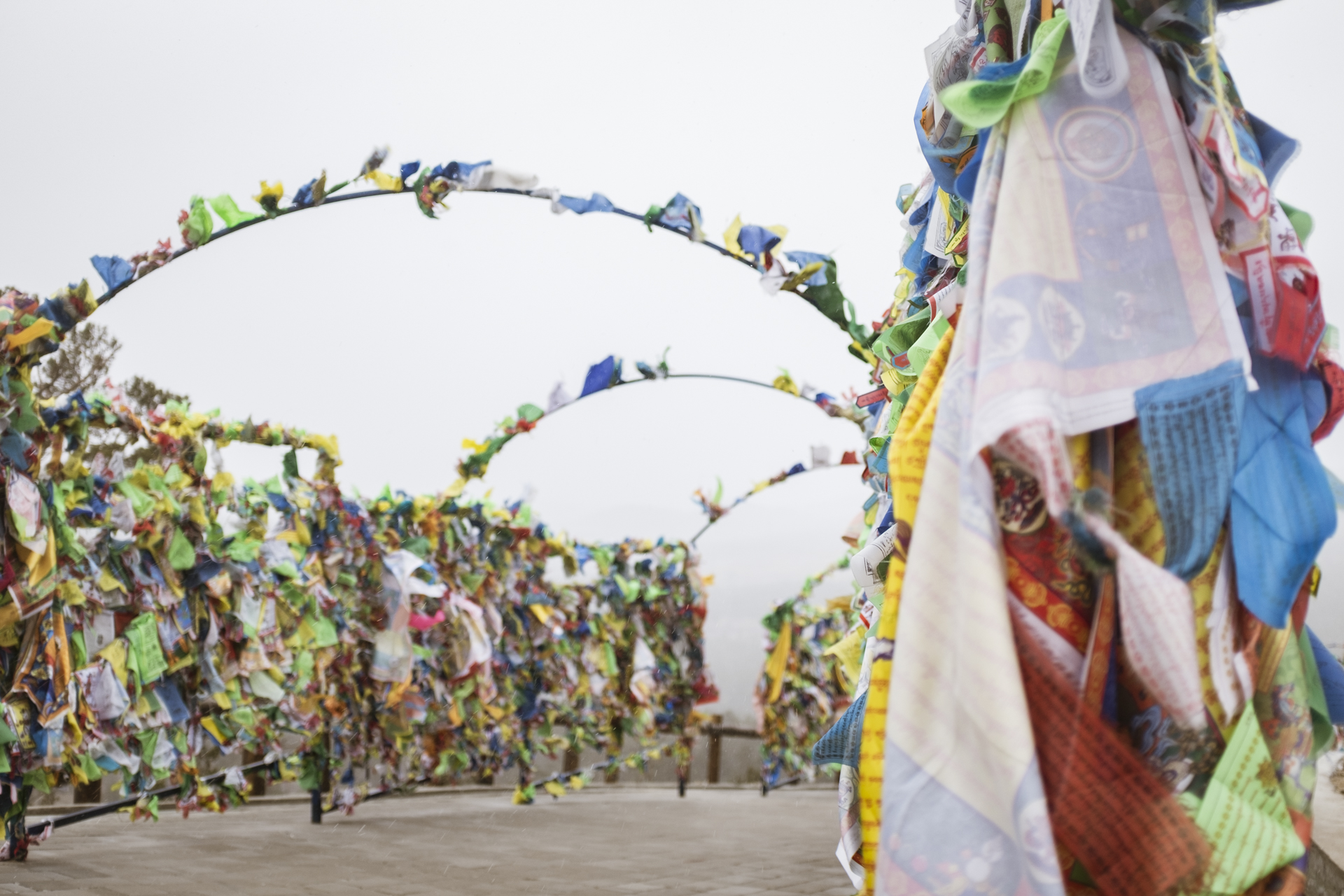
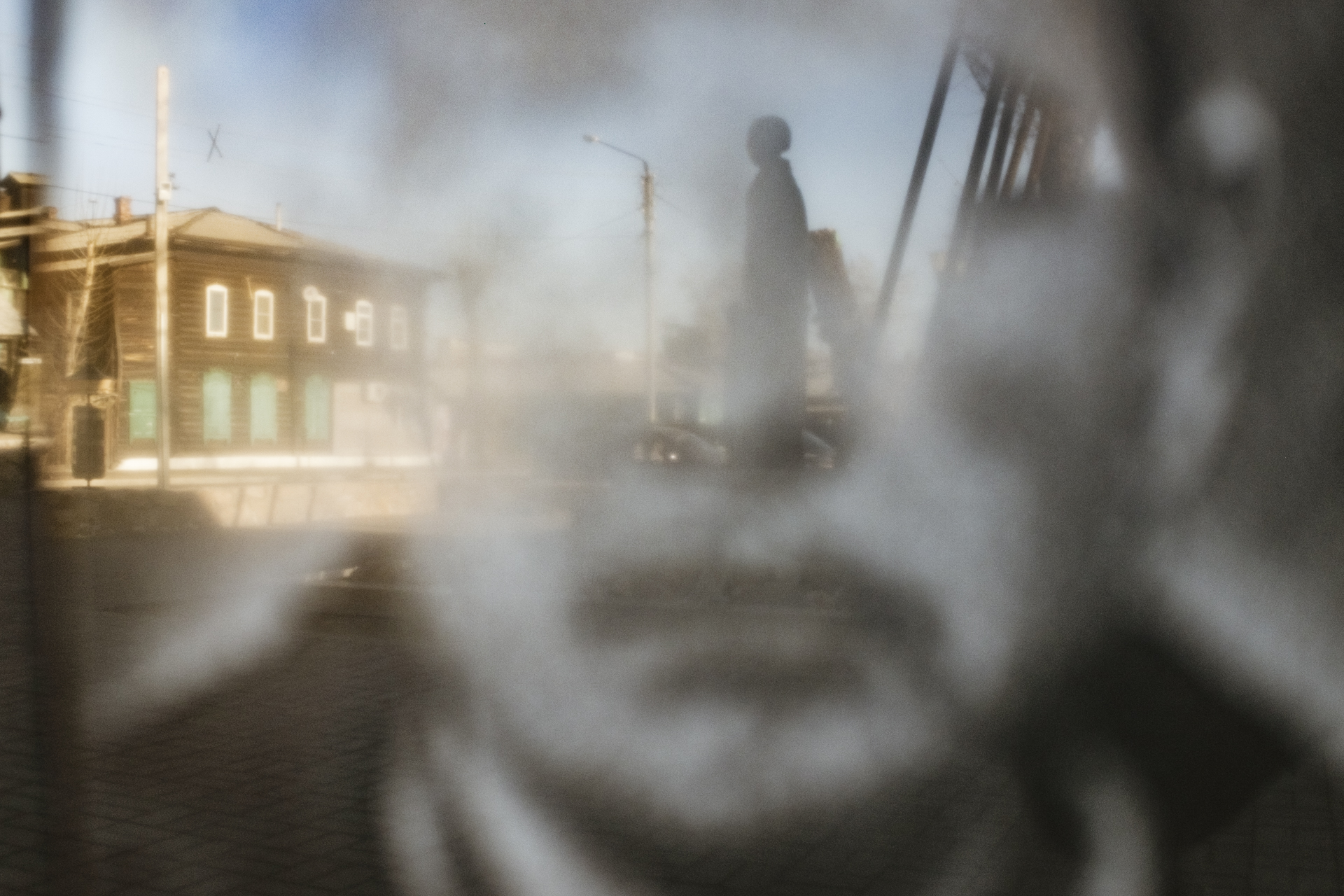
The first thing almost everyone learns about Ulan-Ude is that it’s the home of a monumental sculpture of Lenin’s head, towering above the city’s main square. But there’s another colossal figure that has more significance these days -- the largest Buddha in Russia, perched blissfully above the devotees at Rinpoche Datsan in the hills on the outskirts of the city. Worshippers attend daily services that are alive with drums and chanting and afterwards ask for the blessing of its aging Lama. They can also follow a kilometer-long “Walk of Life” that pays tribute to all the animals of the Buddhist zodiac. (Gabriela is a tiger, and Mark is a bull.) On the morning of our visit, a snowstorm with savage winds cut right through our overly optimistic outerwear and obscured the view of the mountains around us. But a single purple crocus reminded us that Siberia’s next season will arrive eventually.
Back in the center of the city, at the only women’s monastery for Buddhists in Russia, a grinning Lama emphasized the interconnected nature of everything, including the natural world, and the cause and effect nature of our actions. If we throw garbage at Lake Baikal, it will be harmed. In her view, a growing number of birth defects can be traced to the damage people are doing to the environment.
At the Ivolginsky Buddhist Monastery, about 40 kilometers outside of Ulan-Ude, the Rector of the Buddhist University, Dimbril Bagsha Dashibaldanov, also stressed the importance of reverence for all living things -- and traced ecological problems to the human ego. The emotions that arise in the body as a result of egoism, such as anger and dislike and jealousy, are the root causes of environmental degradation, and to the extent we can eliminate these feelings and focus more on other people, such as our neighbors, we can better safeguard the natural world.
When asked about the urgency of responding to critical issues like climate change, Dashibaldanov favored “raising awareness” over anything prescriptive, emphasizing that people need to work on changing themselves instead of being told what to do. Can people change quickly enough? It’s not clear. But he raised the possibility that we need a “фишка” (pronounced “fishka”) -- Russian slang for a transformational idea -- to help improve ecological conditions. He pointed out that it took only a few years for smartphones to conquer the world, and something similar for the environment has the potential to jump-start real progress.
After meeting with the Rector, we strolled the grounds of the Monastery, which was opened in 1945 as the spiritual center of Buddhism in the Soviet Union. Among the many ornate and exceptional buildings on the grounds, one can enter a shrine that contains the body of Dashi-Dorzho Itigilov, a Buryat monk who died and was buried in the lotus position in 1927. According to his own instructions, his body was exhumed 30 years later, and shocked adherents were amazed to see that it was entirely intact with no signs of decomposition. Worried about how the Soviet Union would react, they reburied the Lama, and exhumed him again in 2002, when his body was once again found to be extraordinarily well-preserved. But more than that, many of his followers claim that he is actually alive, in a transcendent state of meditation or nirvana. A jovial monk near the door insisted that Itigilov’s body is warm, that he sweats under his armpits and needs to have his clothes changed, and that his face shows fatigue after long rituals. Visitors were invited to ask the monk for assistance, but cautioned to remember others before thinking of ourselves. We were careful to include Lake Baikal in our prayers.
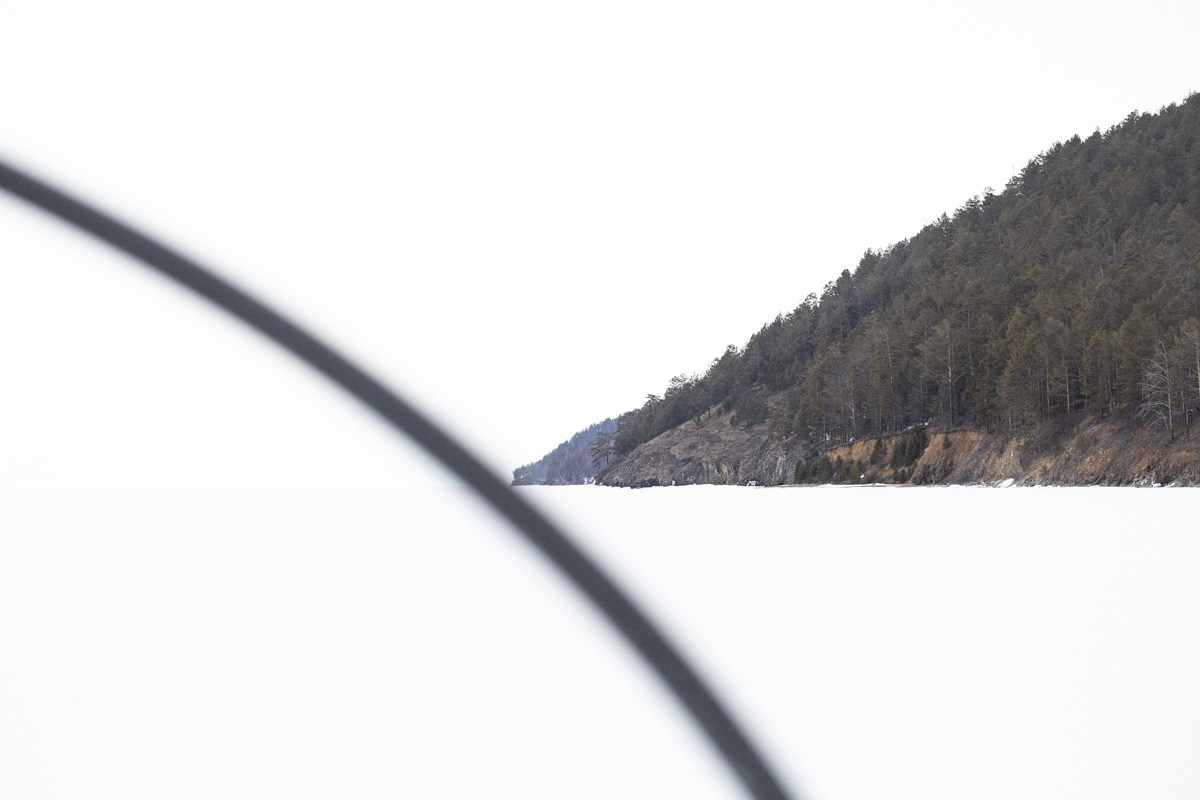
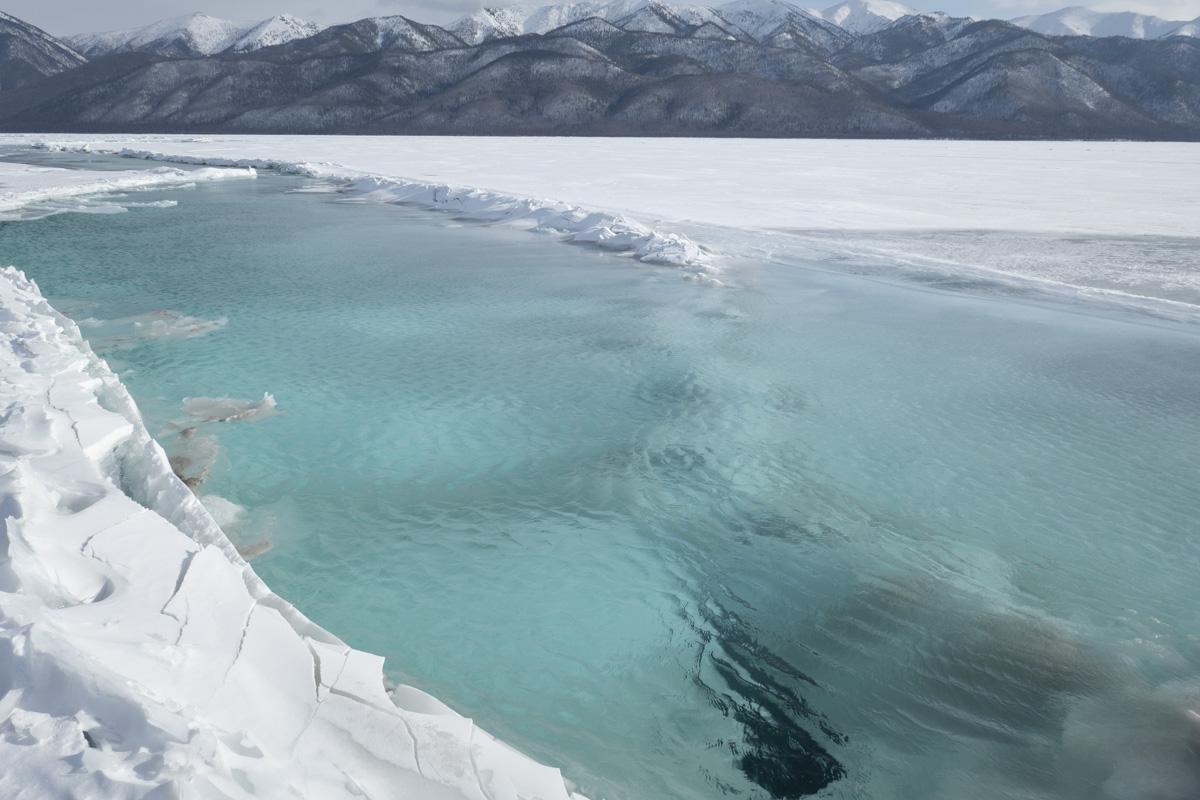
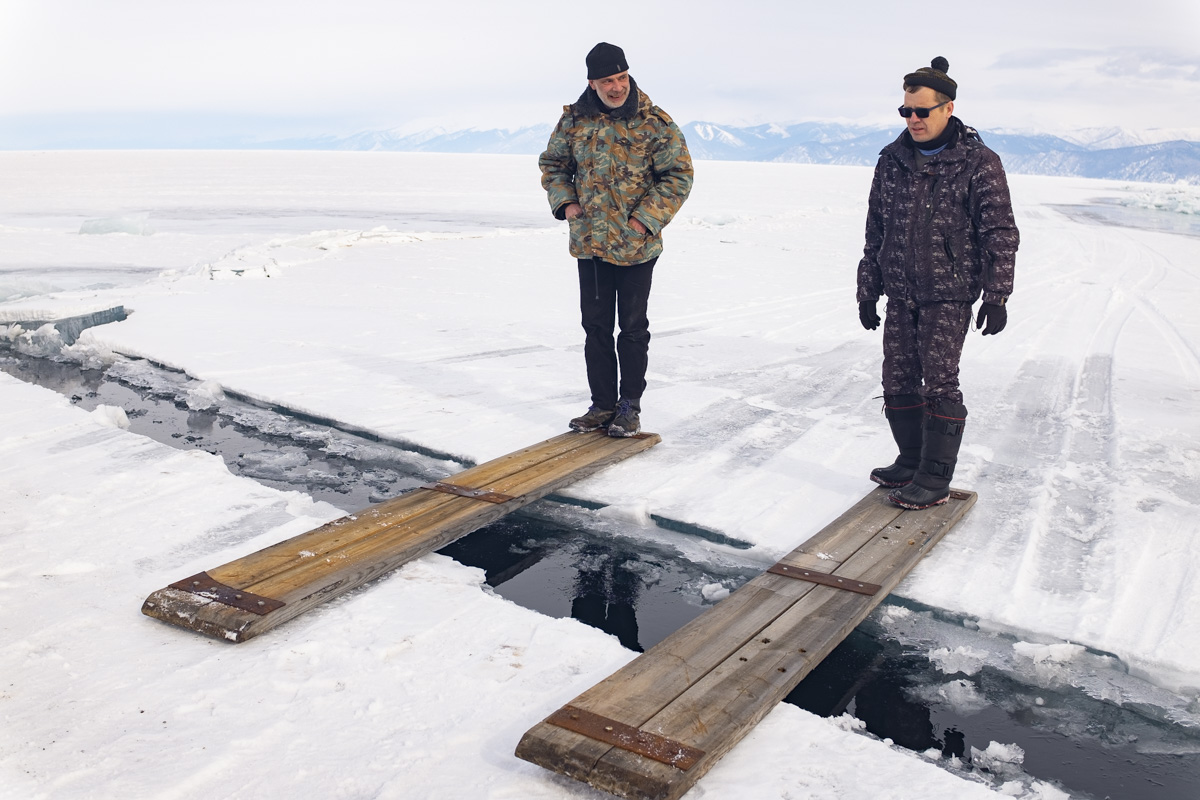
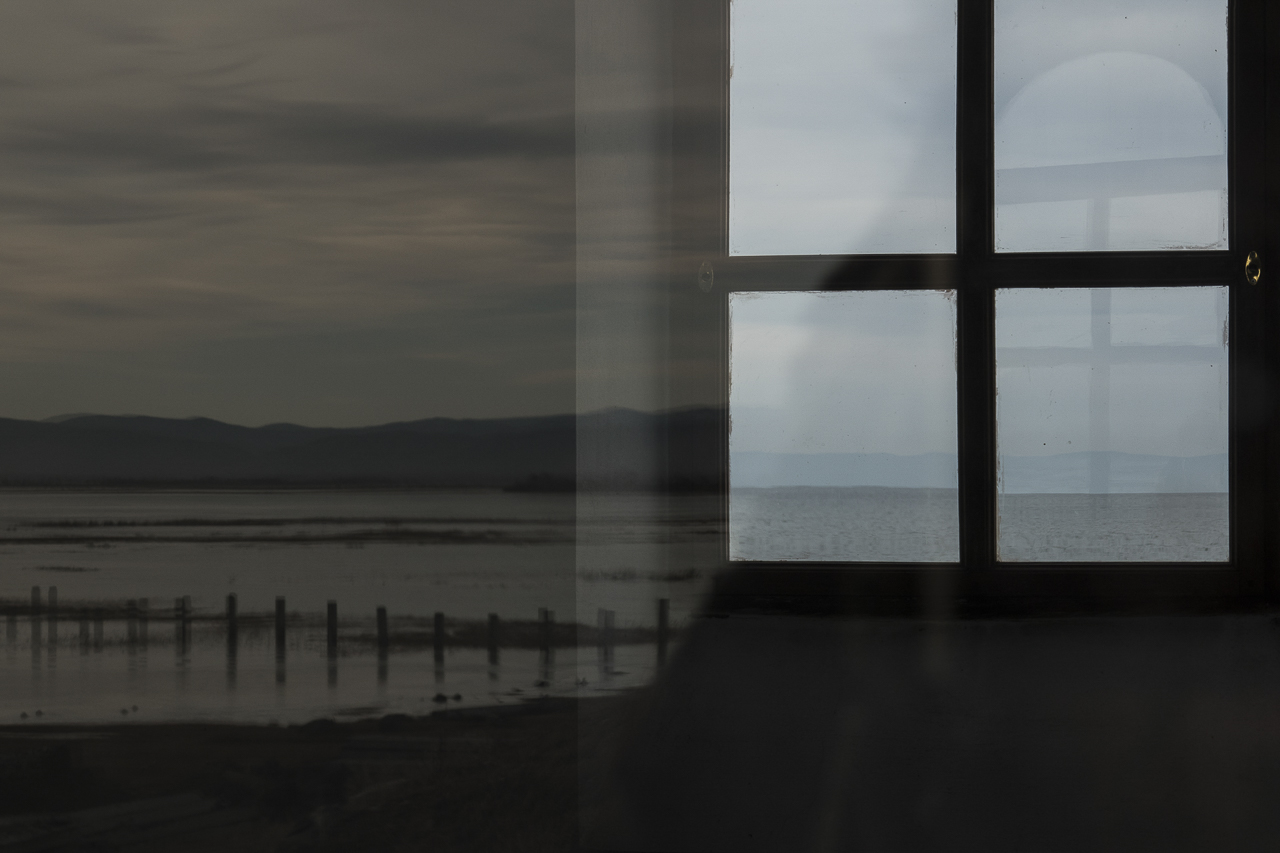
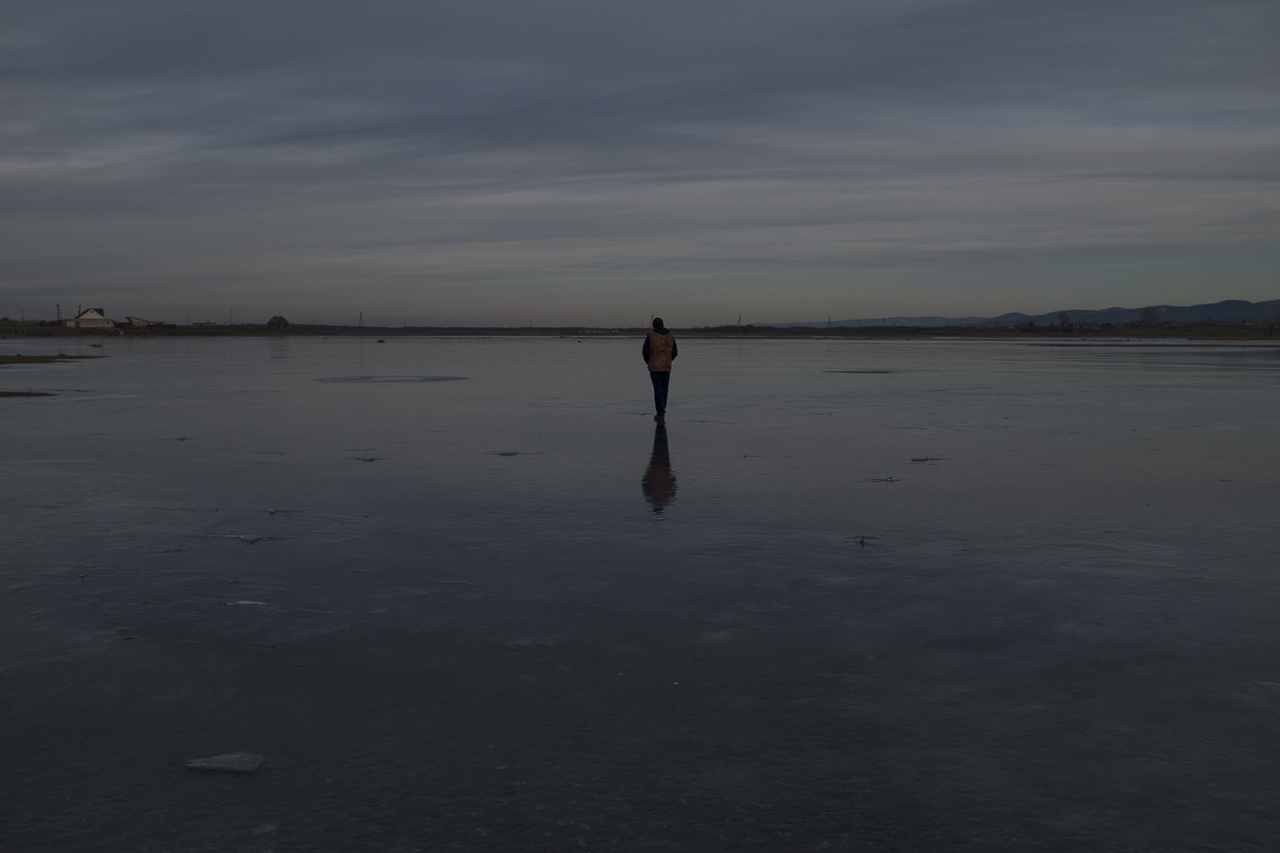
Many Buryats in Russia are Buddhists, many embrace the ancient practice of Shamanism, and still others practice both. But all Buryat traditions are extremely close to the natural world. Marina Danginova, a practicing female Shaman, explained that nature is alive in the Buryat tradition. For example, Baikal is a living organism, and in winter, it goes to sleep rather than freezing. Marina worries a lot about damaging changes in the Baikal region in recent years, including extensive fires, the strong push to create businesses along the Lake’s shores, and the fluctuating level of water in the Lake. “We will not remain silent,” she insisted. But her most important worry is that, as Buryats slowly lose their language, they also lose their connection to nature.
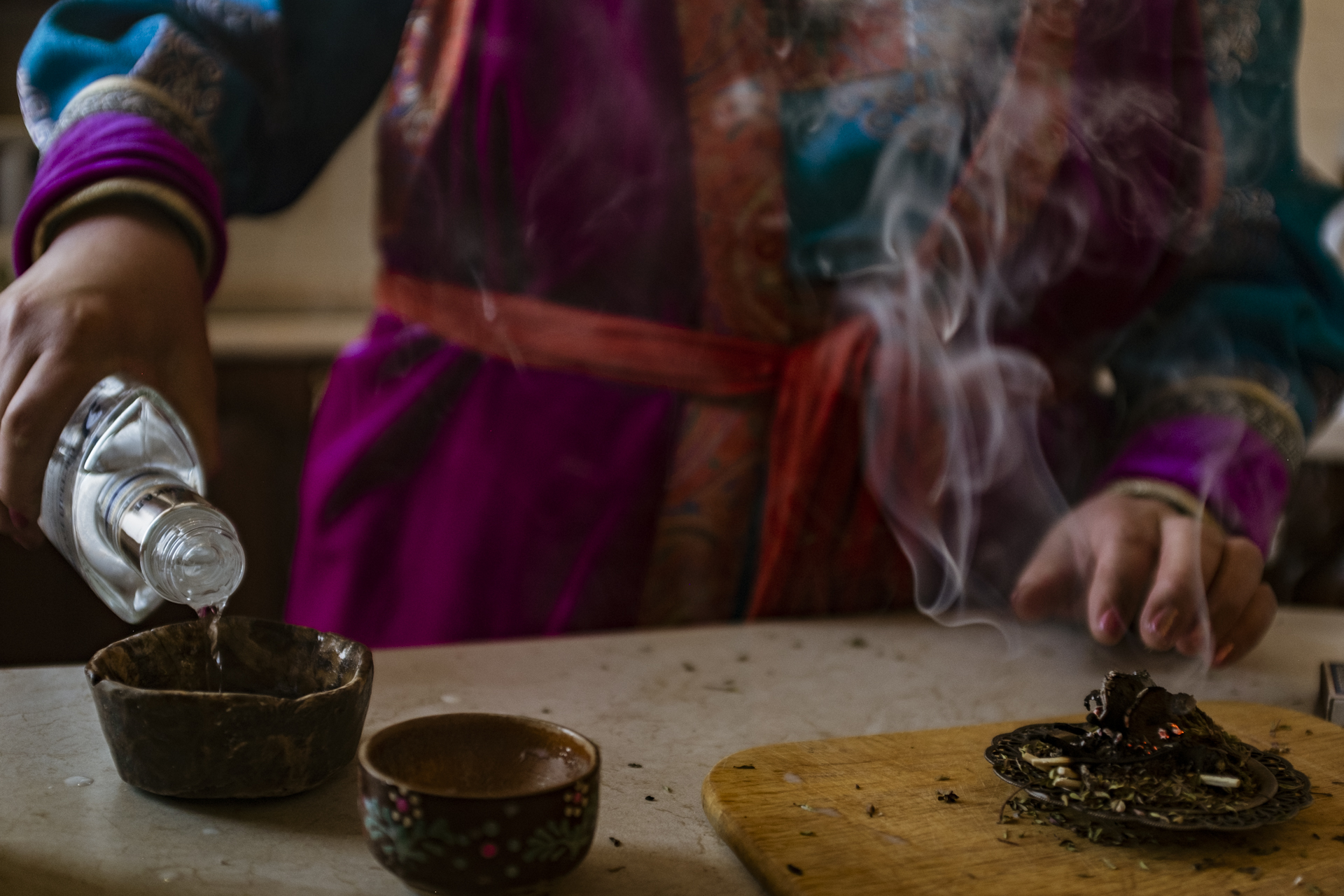
The next day, Marina met us at our Airbnb to conduct a ritual in support of our project. She started by lighting ceremonial Siberian herbs and letting the smoke and the scent permeate the entire apartment. She passed vodka, milk, cookies and candies above the burning herbs. Then she spilled vodka and milk at the window as she chanted in the Buryat language, and mixed these ingredients in a bowl. A cup of black tea made its way into the concoction. The sequence was repeated several times, each time with an empty cup thrown over her shoulder. At the end of the ritual, we were asked to carry the bowl of vodka, milk and tea outside, walk around a tree, and sprinkle the contents at the base. Similar Buryat rituals can also be used to ask for what is needed in the natural world, such as the rain needed by farmers.
It’s not surprising that Buryats commune closely with nature. They are the “original ecologists” who insist on taking only what they need from around them. But we were taken aback when we learned that Metropolitan Sergey Popkov, the youthful leader of Old Believers in Siberia, is an unabashed environmentalist.
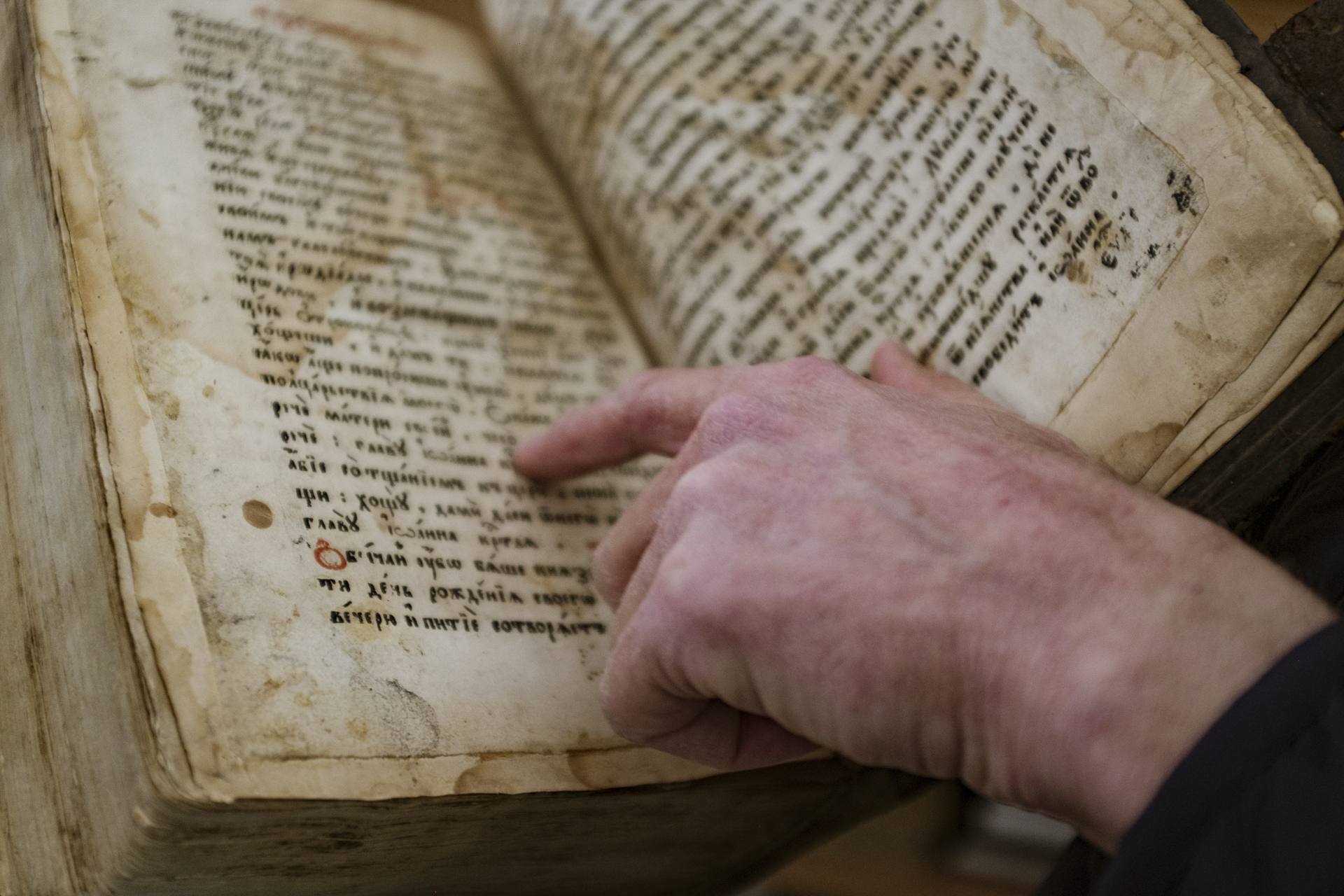
Old Believers resisted reforms that were instituted by the Eastern Orthodox Church in the mid-1600’s, adhering closely to the ancient liturgy and rituals. As a result, they lost their civil rights and were persecuted and even executed. Some fled Russia, and small pockets exist in many places around the world, including the United States. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, Old Believers can freely open churches in Russia, such as the one where Metropolitan Popkov leads his parishioners.
In good English and with no hesitation, the Metropolitan recited a litany of negative environmental changes he has witnessed in recent years, including climate change, an increase in forest fires, reduced groundwater, shallow rivers and streams, diminished fish populations in the Selenge and Ude Rivers, thick smog in the city, expanding problems with garbage, and the spread of non-native species, among others. He acknowledged that many problems, such as the practice of setting fire to woods so that it is then legal to log the wood, stem from a lack of good jobs, so he favors policies that will provide people with more economic security. In his view, climate change is accelerating environmental degradation, in part by driving people to cities, where the link to nature is more tenuous. Much like the Buddhists, he suggested that individuals start by improving their own practices as an important first step. Luckily, humankind’s connection to nature and to God is essentially the same, so it’s possible to enhance both simultaneously.
Following the Buryat ritual in our apartment, we quickly learned that the spirits favored us. There were two auspicious signs. First, liquid spilled on the window traveled straight down. Second, the cup landed face up each time it was thrown. Not only did the spirits welcome us, they had been waiting for us.
Playfully, it seems. After the ceremony, important items disappeared four times, then reappeared in places that had already been searched. The exact meaning of this mischief remains unclear.
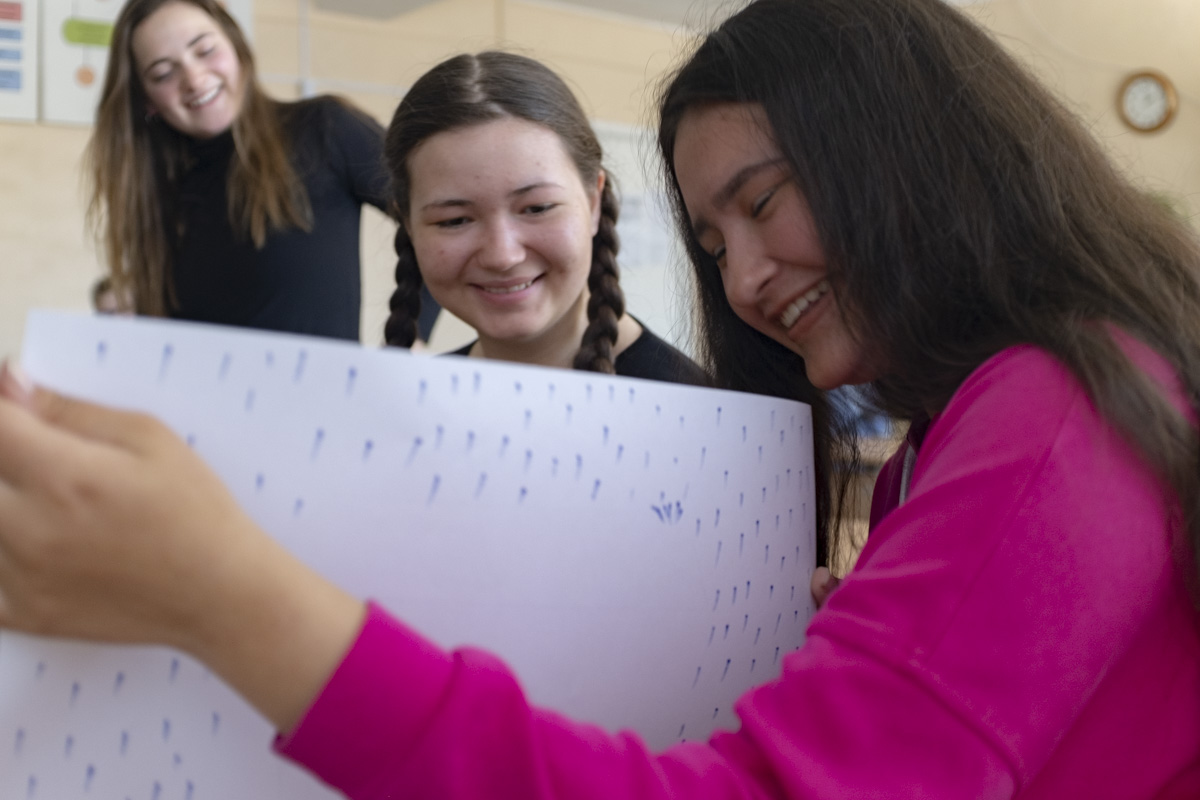
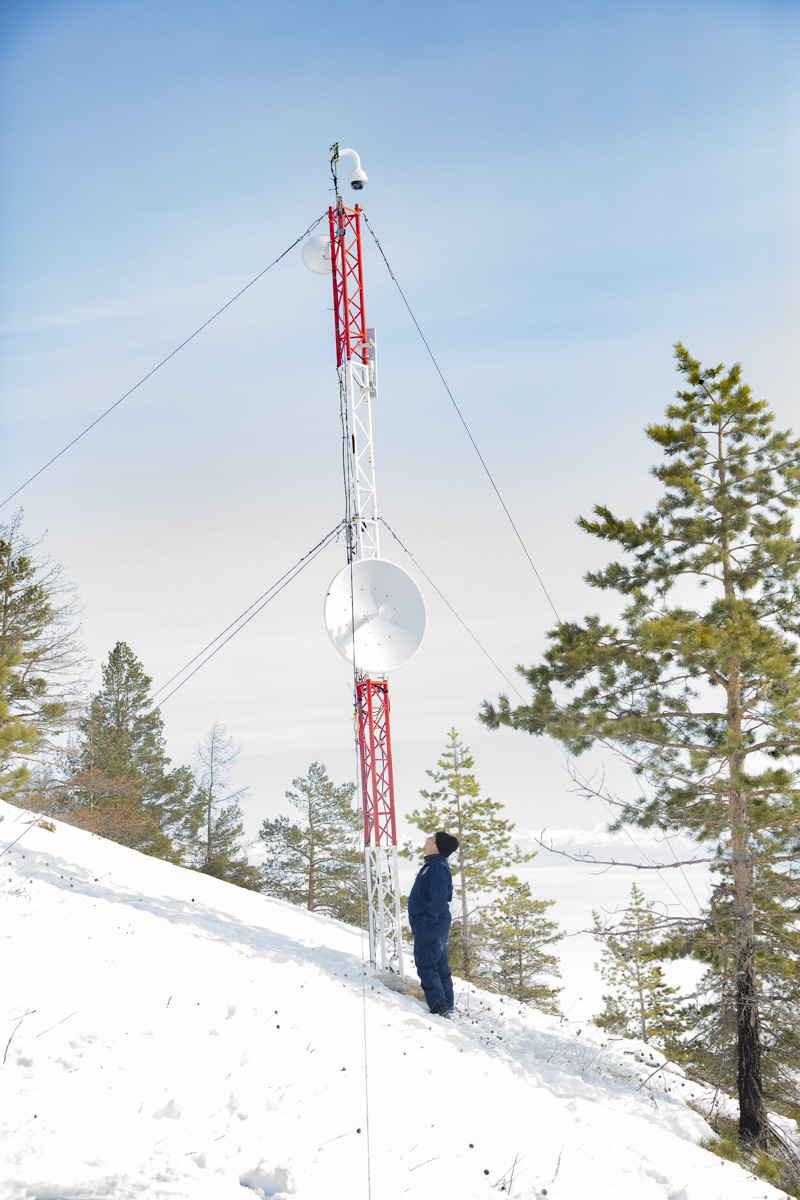
But if the spirits were waiting for us, we were also waiting for them. In Ulan-Ude, almost everything felt spot-on. The team of women from Buryat State University who hosted us were among the kindest and most accomplished people we’ve met in Russia. Their students, who welcomed us in their classrooms and helped us navigate the city, were exceptional guides with outstanding English skills. The Director of the Fulbright Program in Russia, Joel Ericson, arrived in Ulan-Ude complete with a can-do spirit and a concrete vision of how to expand Fulbright’s focus on Baikal and safeguard its future.
Most of all, representatives of every faith greeted us with open arms in successive meetings, embracing diversity and focusing on a better future -- a future in which the health and well-being of the people is never separate from the health and well-being of all living things. The spirits don’t care if you are Orthodox, an Old Believer, a Buddhist, a follower of Shamanic traditions, or an atheist. In Buryatia, it is the nature of faith to safeguard the Earth. The spirits only want us to do the right thing.
In Ulan-Ude, monumental socialist realism meets pop cuisine in this inimitable Lenin head gingerbread.